What is User Experience Design?
User experience design (UX, UXD, UED or XD) is the process of enhancing user satisfaction with a product by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction with the product.[1] User experience design encompasses traditional human–computer interaction (HCI) design, and extends it by addressing all aspects of a product or service as perceived by users.
UX is not UI, then what is the definition of UX exactly? Here I am not going to shoot the cliche but to provide you with a intuitive introduction which will help you to get a quick understanding of why UX is not UI. Good UX designfocuses on the interactive side of the product, how it behaves, such as a box sliding out, and how people might interact with it, such as where they will click first. UX handles the architecture of the content and the site map.
User experience design is a human-first way of designing products. UX, which stands for user experience, is the process of researching, developing, and refining all aspects of a user’s interaction with a company to ensure the company is meeting the user’s needs. A UX designer must ensure people find value when they interact with a company’s products or services.

Elements
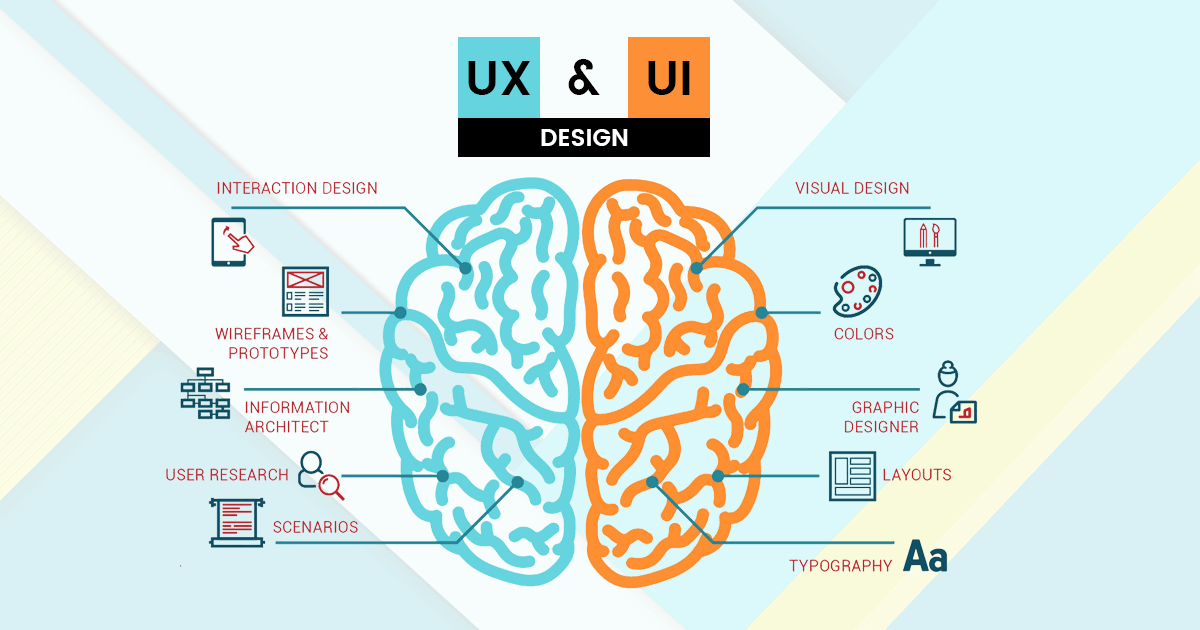
User experience design includes elements of interaction design, visual design, information architecture, user research, and other disciplines, and is concerned with all facts of the overall experience delivered to users. Following is a short analysis of its constituent parts.
Visual design
Visual design, also commonly known as graphic design, user interface design, communication design, and visual communication, represents the aesthetics or look-and-feel of the front end of any user interface. Graphic treatment of interface elements is often perceived as the visual design. The purpose of visual design is to use visual elements like colors, images, and symbols to convey a message to its audience. Fundamentals of Gestalt psychology and visual perception give a cognitive perspective on how to create effective visual communication.
Information architecture
Information architecture is the art and science of structuring and organizing the information in products and services to support usability and findability.
In the context of information architecture, information is separate from both knowledge and data, and lies nebulously between them. It is information about objects. The objects can range from websites, to software applications, to images et al. It is also concerned with metadata: terms used to describe and represent content objects such as documents, people, process, and organizations. Information Architect also encompasses how the pages and navigation are structured.
Structuring, organization, and labeling
Structuring is reducing information to its basic building units and then relating them to each other. Organization involves grouping these units in a distinctive and meaningful manner. Labeling means using appropriate wording and nomenclature to support easy navigation and findability.
Finding and managing
Findability is the most critical success factor for information architecture.[citation needed] If users are not able to find required information without browsing, searching or asking, then the find-ability of the information architecture fails. Navigation needs to be clearly conveyed to ease finding of the contents.
Interaction design
It is well recognized that component of interaction design is an essential part of user experience (UX) design, centering on the interaction between users and products. The goal of interaction design is to create a product that produces an efficient and delightful end-user experience by enabling users to achieve their objectives in the best way possible
** Defining interaction patterns best suited in the context
** Incorporating user needs collected during user research into the designs
** Features and information that are important to the user
** Interface behavior like drag-drop, selections, and mouse-over actions
** Effectively communicating strengths of the system
** Making the interface intuitive by building affordances
** Maintaining consistency throughout the system.
** Utilizing a haptic feedback system to reduce confusion
In the last few years, the role of interaction designer has shifted from being just focused on specifying UI components and communicating them to the engineers to a situation now where designers have more freedom to design contextual interfaces which are based on helping meet the user needs. Therefore, User Experience Design evolved into a multidisciplinary design branch that involves multiple technical aspects from motion graphics design and animation to programming.
Usability
Usability is the extent to which a product can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction in a specified context of use.
Usability is attached with all tools used by humans and is extended to both digital and non-digital devices. Thus, it is a subset of user experience but not wholly contained. The section of usability that intersects with user experience design is related to humans’ ability to use a system or application. Good usability is essential to a positive user experience but does not alone guarantee it.
Usability testing
Usability testing is a technique used in user-centered interaction design to evaluate a product by testing it on users. This can be seen as an irreplaceable usability practice, since it gives direct input on how real users use the system. It is a measure of how fast a user can perform given tasks to test the efficiency and intuitiveness of a product.
Accessibility
Accessibility of a system describes its ease of reach, use and understanding. In terms of user experience design, it can also be related to the overall comprehensibility of the information and features. It helps shorten the learning curve associated with the system. Accessibility in many contexts can be related to the ease of use for people with disabilities and comes under usability.
What is User Experience Design?
User interface design (UI) or user interface engineering is the design of user interfaces for machines and software, such as computers, home appliances, mobile devices, and other electronic devices, with the focus on maximizing usability and the user experience. The goal of user interface design is to make the user’s interaction as simple and efficient as possible, in terms of accomplishing user goals (user-centered design).
Good user interface design facilitates finishing the task at hand without drawing unnecessary attention to itself. Graphic design and typography are utilized to support its usability, influencing how the user performs certain interactions and improving the aesthetic appeal of the design; design aesthetics may enhance or detract from the ability of users to use the functions of the interface. The design process must balance technical functionality and visual elements (e.g., mental model) to create a system that is not only operational but also usable and adaptable to changing user needs.
Interface design is involved in a wide range of projects from computer systems, to cars, to commercial planes; all of these projects involve much of the same basic human interactions yet also require some unique skills and knowledge. As a result, designers tend to specialize in certain types of projects and have skills centered on their expertise, whether that be software design, user research, web design, or industrial design.

Design isn’t all about learning to use design software —although that’s certainly important. Software is like a designer’s sword. You need the sword to fight the battle, but that’s not all you need to learn to use. You need to learn the strategies, processes, tricks and tips of the fight/game to be able to win it. In UI design, you need to brainstorm, experiment, test, and understand your users and their journey throughout using your product.
The benefits of having a well-designed product is that you’ll have a higher user retention rate.
** On a screen, people will always read the biggest, the boldest, and the brightest first. This is human nature. Our attention is programmed in such a way where we see the biggest, the boldest, and the brightest first. And then it moves to smaller, less bold, and less bright things.
** The Importance of Alignment. Alignment is a fundamental aspect of UI Design. And an important design principle is: minimize the number of alignment lines. It improves readibility and makes the design more pleasing to the eye.
Become an attention architect
Here’s two ways to interpret this: 1) You need to grab the user’s attention with your design. 2) You need to pay attention to every little thing in your designs.
To be a great designer, you need to do both. The latter lets you achieve the former.
UI Design is about tailoring the experience for your users by guiding their attention towards different important things.
Ways to use text to grab user’s attention:
** Make its size larger or smaller.
** Bolder or brighter in color. Or make it muted.
** Use a typeface with a heavy weighting versus something that is thin or light.
** Italicize words. Capitalise or lowercase some words.
** Increase the distance between each of the letters to make the overall size of the words take up more space.
The most important thing when designing is testing! Make sure you try out different everything: colors, fonts, tones, angles, alignment, layout, etc. Experiment with different designs so that you can architect a user journey using various ways of commanding attention.
